The employment landscape in Vietnam has undergone significant changes over the years, influenced by various factors such as economic growth, industry developments, and the impact of the Covid-19 pandemic. This comprehensive report explores the trends and key aspects of employment in Vietnam from 2008 to the present time. It covers crucial areas including the labor force, salary levels, and unemployment rates, providing valuable insights into the evolving employment scenario in the country.
I.Employment in Vietnam:
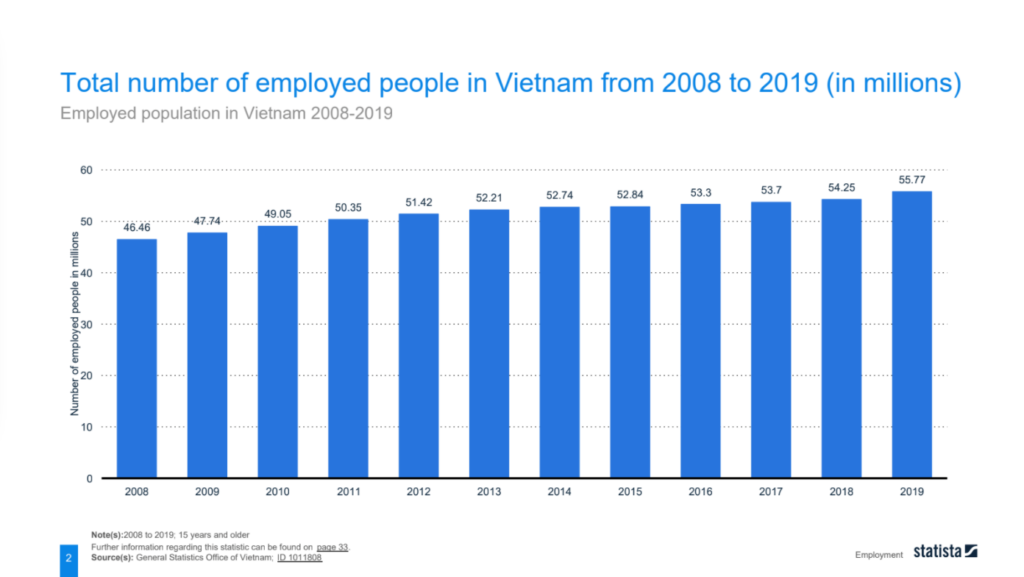
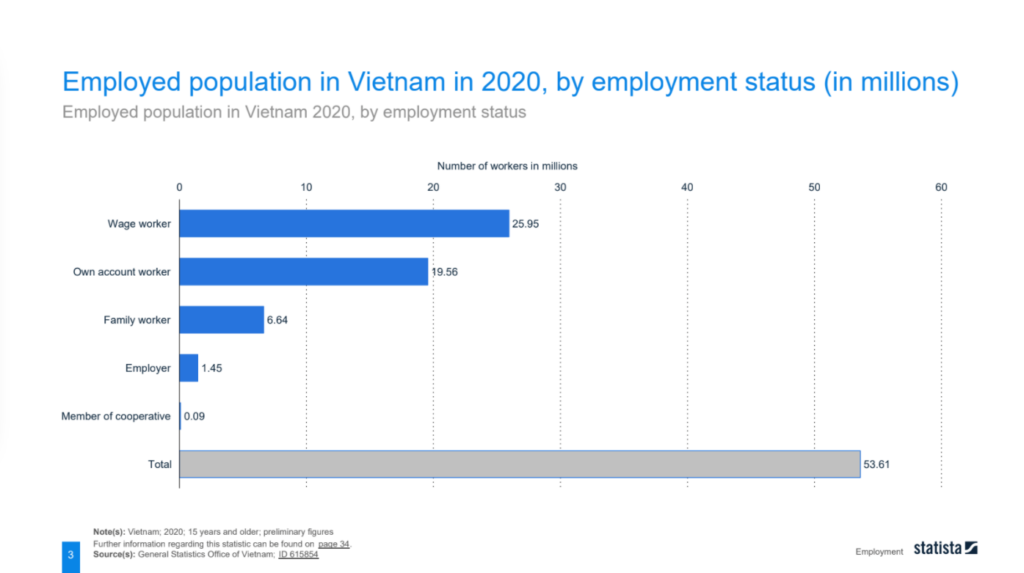
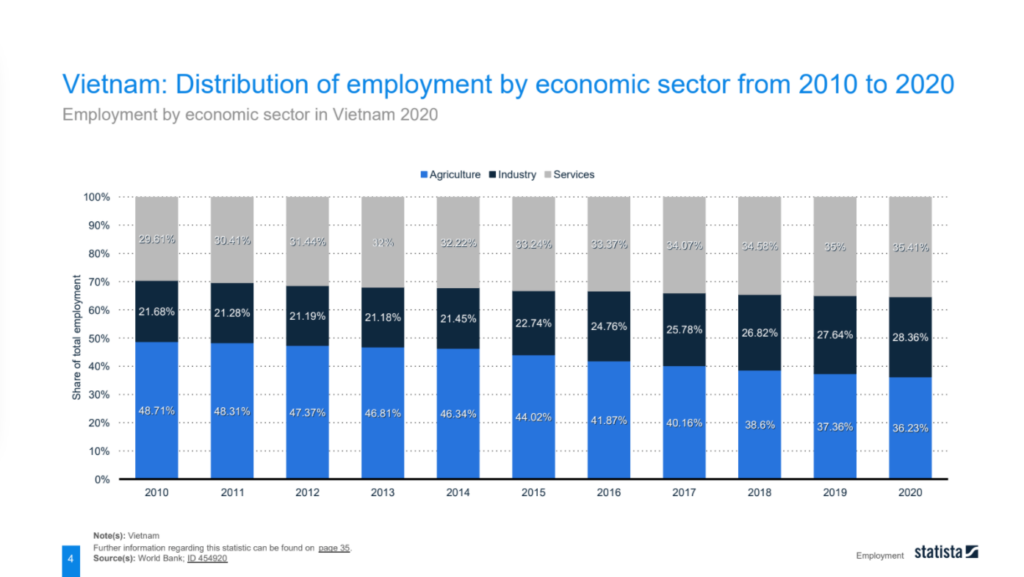
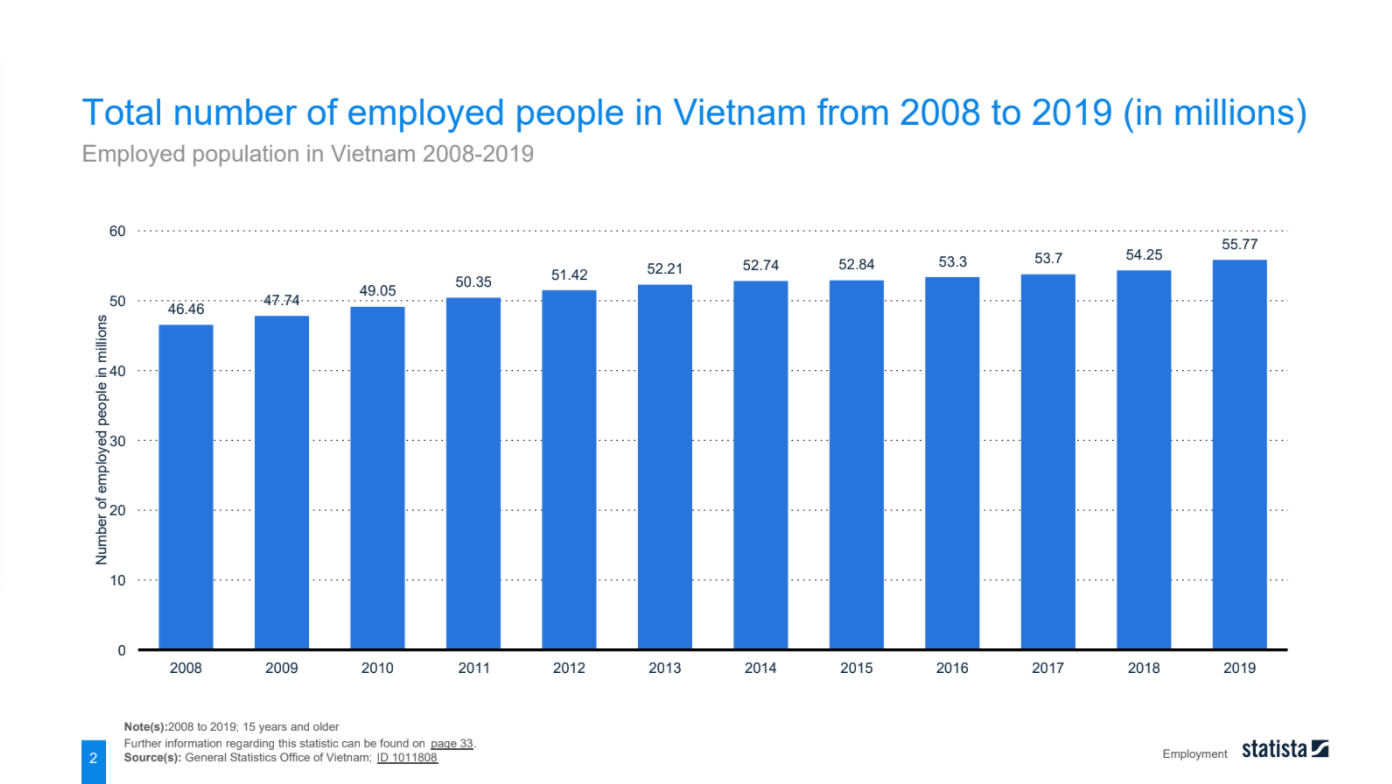
The labor force in Vietnam has witnessed substantial growth, increasing from 46.46 million in 2008 to 55.77 million in 2019. This growth can be attributed to various factors, including population growth, economic development, and increased participation in the workforce. The employment distribution comprises wage workers, self-employed individuals, family workers, employers, and cooperative members. The agriculture sector accounted for a significant portion of employment in 2010, reflecting the country’s agrarian economy. However, over the years, there has been a notable shift towards the industry and service sectors, indicating the diversification of the economy.
II.Labor Force:
The labor force in Vietnam displayed steady growth throughout 2019, with an increase of 4.52 million people from the first quarter to the fourth quarter. This growth reflects the expanding job market and the ability of the economy to generate employment opportunities. The distribution of the labor force showed a higher concentration in rural areas compared to urban areas, highlighting the importance of agriculture and rural industries in providing employment. However, urban areas also experienced significant growth in the labor force, driven by industrialization and urbanization. The labor force participation rate fluctuated, with rural areas consistently exhibiting higher rates than urban areas, indicating the differences in economic activities and opportunities between the two regions.
III.Salary:
Average monthly salaries for paid workers in Vietnam varied across sectors and regions. The salary levels were influenced by factors such as job type, education level, skills, and experience. Male workers generally earned higher salaries than their female counterparts, reflecting gender disparities in the job market. Urban areas had higher average salaries compared to rural areas, which can be attributed to the concentration of higher-skilled and better-paying jobs in urban centers. However, there were variations observed throughout the year, reflecting the dynamic nature of the job market and economic conditions. Salary growth in different industries also varied, with the technology sector showing the highest growth in 2019, reflecting the growing demand for skilled professionals in the digital economy.
IV.Unemployment:
The unemployment rate in Vietnam remained relatively stable around 2% during the period under review, indicating a relatively low level of unemployment. However, there were slight fluctuations over time, reflecting the impact of economic conditions and business cycles. The youth unemployment rate, specifically, experienced an increase from 3.4% in 2011 to 7.6% in 2020, indicating the impact of the Covid-19 pandemic on young workers. This increase can be attributed to factors such as job losses, reduced hiring, and the challenges faced by young job seekers in a competitive job market. The government implemented various measures to address youth unemployment and provide support to affected individuals. Unemployment insurance expenditure decreased in 2020 compared to previous years, reflecting the lower number of individuals claiming unemployment benefits due to improved economic conditions. Similarly, revenue from unemployment insurance also experienced a decline, reflecting the lower demand for unemployment insurance coverage.
In conclusion, the employment landscape in Vietnam has experienced significant transformations over the years. The labor force has grown, with changes observed in the distribution among sectors and regions. Salary levels have shown variations based on factors such as industry and location. The Covid-19 pandemic has had a notable impact on youth unemployment rates and unemployment insurance expenditures. These insights into employment trends provide a comprehensive understanding of the evolving labor market in Vietnam.
Key Points Summary:
- Vietnam’s labor force has grown, with a shift from agriculture to service and industry sectors.
- Salary levels vary based on industry, education level, and geographic location.
- The Covid-19 pandemic has impacted employment, particularly youth unemployment.
- The report highlights the resilience of Vietnam’s labor market.
For further information or personalized assistance, feel free to contact our Vietnam team.
Leave a Reply